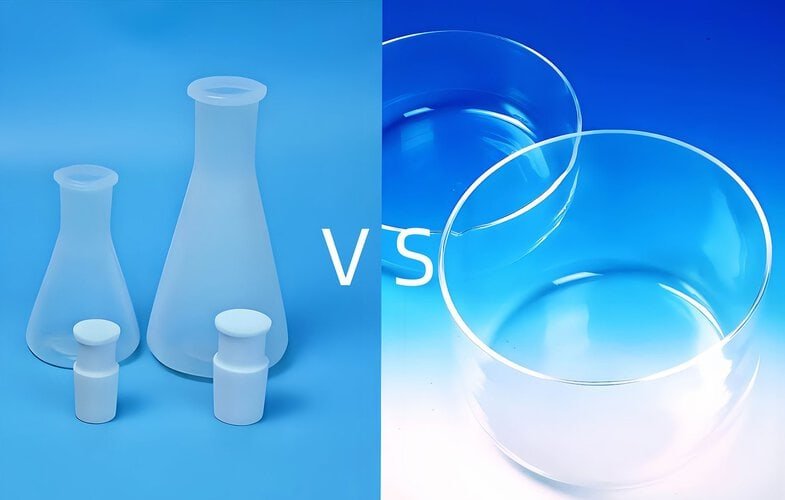
Quartz Glass
The main component of quartz glass is high-purity silicon dioxide. Its most prominent advantages lie in its extremely high thermal stability and excellent optical transparency. It can withstand high temperatures above 1000 ° C for a long time and can be used even higher in a short period of time, making it an ideal choice for high-temperature burning, ashing, and tube furnace reactions. At the same time, it has extremely high transmittance from ultraviolet light to infrared light, making it the preferred material for ultraviolet light cells and optical components. It has good chemical stability and can withstand most acids except hydrofluoric acid and hot phosphoric acid. But its main disadvantages are high brittleness, lack of resistance to impact and rapid cooling and heating (although its thermal shock performance is better than ordinary glass, caution is still needed), and inability to resist the corrosion of hydrofluoric acid.
Fluoroplastics (such as PTFE/PFA)
The core advantage of fluoroplastic containers, such as PTFE and PFA, is unparalleled chemical inertness. They can resist almost all highly corrosive chemicals, including aqua regia and hydrofluoric acid, and are the cornerstone for handling ultra pure and sensitive samples. Another key characteristic is the extremely low surface energy, which ensures that the sample does not adhere and is easy to clean, effectively preventing cross contamination. PFA also has good translucency, making it easy to observe the reaction process. Their main limitations are low temperature resistance (PTFE has a continuous use temperature of about 260 ° C, PFA has a temperature of about 180 ° C), and their mechanical strength is relatively soft, making them easy to scratch.
Choose quartz glass: When your experiment involves high temperatures (>300 ° C), optical applications, or requires rigid vessels.
Choose fluoroplastics: When your experiment involves hydrofluoric acid, ultra-high purity reagents, trace analysis, or requires excellent anti pollution properties.
In short, quartz glass is the “heat-resistant perspective expert”, while fluoroplastics are the “anti-corrosion and non stick guardians”. Making a choice based on the core requirements of the experiment – whether it is extreme temperature or extreme corrosion – is the key to ensuring the success and safety of the experiment.